|
|
 |
Vu Bang
Vice Chairman, State Securities Commission
PART I
INTRODUCTION TO THE VIETNAMESE SECURITIES MARKET
I. The establishment of the State Securities commission
After 15 years of renovation, Vietnam has made remarkable achievements.
GDP had grown at the average annual rate of 8.2% for the period from 1991
to 1999 and of approximately 7% for the years 2001 and 2002. The ratio
of investment to GDP reached more than 34%. In order to mobilize capital
for national industrialization, modernization and enhancement of economic
efficiency, the government of Vietnam has paid special attention to the
development of securities markets. For the early establishment of securities
market, the government decided to set up the State Securities Commission
at the end of 1996. The commission is an independent body of the government,
with the regulatory functions in the field of securities and securities
markets. The State Securities Commission is responsible for development
of legal framework for securities and securities market as well as regulatory
functions of institutions participating in the market, which include surveillance
and inspection, licensing and revoking licenses for listed companies,
securities companies, custodians…. and regulation of securities
trading centers.
II. The process of equitization and bond issuance
1. Equitization
According to approximate statistics, as of 31 December 2002, there had
been more than 1076 State owned enterprises or parts thereof having been
completely equitized and ownership-diversified. For the year 2002 alone,
there were 189 SOEs equitized. Most of the SOEs implementing ownership
conversion in 2002 were small and medium sized ( average charter capital
of VND 4 billions).
The primary stock market has been in existence since the 90s. Before
the promulgation of the Enterprise Law (before 2002), there had been only
more than 200 joint stock companies country-wide, established under the
Company Law, most of them had charter capital less than VND 5 billion
and these companies did not initially raise funds through public offerings
but private placements. There were rarely any secondary stock issuance
or, if any, conducted among existing shareholders. Since the enactment
of Enterprises Law effective since 01 January 2000, the number of joint
stock companies have increased, thanks to innovative amendments to the
previous Company Law. According to the reports by the Enterprise Information
Center ( Ministry of Planning and Investments), in 2000, there were 726
joint stock companies established countrywide with total charter capital
of VND 1550 billions; in 2001 as a result of renovation of the business
registration procedure, the number of newly established joint stock companies
increased significantly reaching 1534 with total charter capital of VND
7 552 billions.
2. Bond Issuance
Currently only government bonds are regularly issued, and mostly through
auction at the Securities Trading Center with the maturities ranging from
5 years to 10 years and at interest rates of 7% for the 5 year maturity
and 9.2 % for the 10 year. Within 2 years, the total amount of bonds issued
through the securities trading center reached VND 3000 billions.
Besides, the government bonds have been also issued through underwriting
and retail distribution. However none of these two modes of issuance are
popular, regular and efficient.
The corporate bond market has been modest. So far only the Bank for Investment
and Development has issued long term bonds to the public and enlisted
them at the Securities Trading Center with the total amount listed of
VND 1069 billions. Apart from that a number of financial and credit institutions
had also issued bonds to the public, such as bond issuance by Vietnam
International finance company VILC, the Vietnam Industrial and Commercial
Bank acting as an issuing agent for issuance of bonds worth VND 2 billions
with the maturity of 2 years, and the issuance of municipal project bonds
by Hochiminh city.
III. The HoChiMinh city securities trading center
1. The HoChiMinh city securities
trading Center (TTGDCK TPHCM) was established by the decision number 127/1998/QQDD-TTg
dated 11 July 1998 by the Prime Minister, it is a non-profit organization
under the direct administration and regulation of the State Securities
Commissions with the following main functions and tasks:
- Organize, manage, operate the securities trading system,
- Perform the functions of custody, clearing, settlements for securities
transactions,
- Conduct examinations, supervision of the securities trading activities,
After preparation, on 20th July 2000 the TTGDCK TPHCM was officially
opened. Since then the TTGDCK TPHCM has conducted more than 400 trading
sessions with the total transactional value of VND 1000 billions.
2. Listed securities at the TTGDCK TPHCM
2.1 Listing criterion
Companies that wish to list their stocks at the TTGDCK shall meet the
following criterion:
- Minimum charter capital of0 VND 10 billions
- Being profitable for the last 2 years
- At least 100 outside investors owning no less than 20 % of equity
capital
- The founding shareholders owning no less than 20 % of equity capital
- Sound financial condition, financial statements to be audited by an
independent auditor.
2.2 Listings at the TTGDCK TPHCM
As of February 2003, there are 21 joint stock companies with the total
market capitalization of VND 3000 billions and 43 types of bonds of the
same amount listed at the TTGDCK TPHCM.
The listed companies are all profitable and have bright prospective;
their profit growth for the year 2002 ranged from 20 to 40% per annum;
on top of that, listed companies in the center have been benefiting from
the preferential tax treatments, which have made dividend payout attractive
to investors.
3. The membership system at the TTGDCK
Securities companies in Vietnam must be joint stock or liability limited
companies licensed by the State Securities Commission as they meet all
the licensing criterion in terms of professional skills, facilities, and
capital ( VND 43 billions for a comprehensive license).
Members of the TTGDCK are securities companies licensed for brokerage,
proprietary trading, and registered as members of the TTGDCK. Only members
are allowed to trade securities at the TTGDCK, are subject to membership
rules set by the State Securities Commission and TTGDCK.
Members are allowed to conduct the following businesses:
- Brokerage
- Proprietary trading
- Portfolio management
- Securities investment advisory
- Underwriting
Currently, TTGDCK has 10 member securities companies and is expected
to admit some more members to meet the need of future market development.
4. Trading system
Currently, 2 mechanisms of trading are allowed:
- Periodic call auction: 5 morning sessions per week on Monday, Tuesday,
Wednesday, and Friday from 9 to 10 am. Orders are matched once every
session at 10 am. The unit of trading is round lot (100 shares or the
multiples thereof, the minimum face value of VND 10000). The trading
band is ± 5%.
- Off - the- book negotiated transaction: from 10 am to 10:20 am (20
minutes after the official call auction is finished) and applicable
to block trades.
5. Custody, Clearing, settlement system
All the securities eligible for trading shall be mobilized at the TTGDCK.
The delivery of securities is made in the form of book entry transfer.
Money settlement is conducted through the designated settlement bank (
the Bank for Investment and Development). The settlement cycle is T+3.
The 10 member securities companies are also custody members of the TTGDCK,
and there are 3 foreign banks licensed as foreign custodians to foreign
individual and institutional investors in the TTGDCK.
6. Information disclosure
Information disclosures are governed by the Regime on membership, listing,
and information disclosure and securities transactions (at the securities
trading center), which specify the obligations of the TTGDCK, listed companies
and fund management companies in information disclosures.
7. Tax regime
- To provide incentives for market participants, at the initial stage
the government provide for the following preferential tax treatment:
- To securities companies and fund management companies: in addition
to tax preferential treatments provided for in the Corporate Income
Tax Law, the institutions are to further benefit from 1 year exemption
from corporate income tax and 50% reduction thereof for 2 years afterwards.
Further more, the Value Added tax is exempted.
- To securities issuers whose stocks are listed in the center, beside
existing incentives, there is also 50% corporate income tax reduction
for 3 years.
- Individual securities investors are exempted from paying personal
income tax for high income class on dividends, bond’s interest
payments, and capital gains.
- Foreign individual securities investors are exempted from paying personal
income tax.
- Income tax rate applicable to foreign institutional investors is 10%.
- Institutions, individuals who buy and sell securities in Vietnamese
securities market are to pay income repatriation tax of 5% on the income
repatriated abroad.
8. Fees
To provide incentives for participants in the market, for the first 2
years the State Securities Commission did not request for securities company
license fees. From that beginning of 2003, the securities company license
fee is set at VND 86 millions for 4 types of licenses and VND 10 millions
for the fund management license. Additionally, TTGDCK have levied any
fees on the members except for the annual fee of VND 20 millions for use
of equipment and facilities (effective from January 2003). Currently securities
companies apply transaction fee of 0.3% of clients’ transaction
value.
9. Foreign participation
- According to the Domestic Investment Promotion Law, foreign investors
are allowed to buy shares face-valued up to 30% of charter capital of
companies.
- In case of listed companies, foreign institutional and individual
investors are allowed to hold up to 20% of outstanding shares of a listed
issuer.
- Procedures and formalities applied to foreign investors in securities
market:
Foreign investors who wish to invest in Vietnamese securities market
shall open an account for securities transactions at a foreign custody
member ( a foreign commercial bank admitted as a custody member of the
TTGDCK).
A foreign custody member shall apply for a trading code with the TTGDCK,
and also acts as an investor’s representative who will place orders
through a member securities company.
- Foreign exchange regime:
The foreign currencies brought in by foreign investors for investment
in securities shall be converted into VND through a foreign custody
member for trading.
When an investor would like to repatriate his/ her profit abroad, a
foreign custody member will resell the foreign currency to the investor
and conduct the transfer of the money for repatriation after the investor
has fulfilled all of his tax and fee obligations.
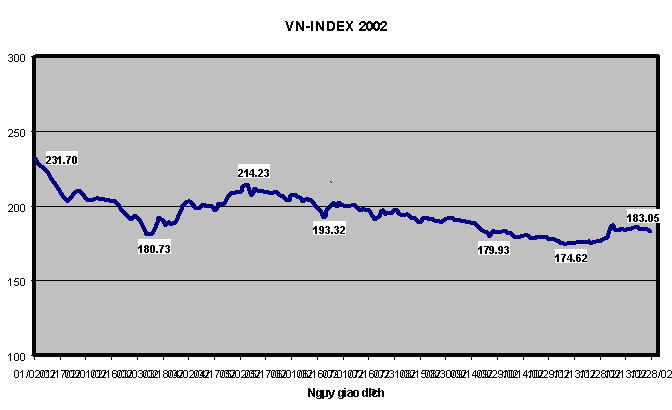
10. VN-Index in 2002
In 2002, the condition of Vietnamese securities market are relatively
quiet, the transaction value shrunk, VN-index dropped. The chart below
depicts the VN-index for the year 2002.
11. Legal framework for the securities market
- Enterprise Law
- Decree 75/NDD-CP dated 28 Nov. 1996 of the Government on the Establishment
of the State Securities Commission.
- Decree 48/1998/NDD-CP dated 11 July 1998 of the Government on securities
and securities markets.
- Rules on organization and operation of securities companies ( promulgated
in conjunction with Decision 04/1998/QDD-UBCK3 dated 13 October 1998
by the Chairman of the State Securities Commission)
- Rules on organization and operation of securities investment fund
and fund management companies ( promulgated in conjunction with Decision
05/1998/Q§-UBCK3 dated 13 October 1998 by the Chairman of the State
Securities Commission)
- Rules on membership, information disclosure and securities transactions
( promulgated in conjunction with Decision 04/Q§-UBCK3 dated 27
March 1999 by the Chairman of the State Securities Commission)
- Rules on securities custody, clearing, settlements, and registration
( promulgated in conjunction with
- Rules on Surveillance, inspection of securities and securities markets
( promulgated in conjunction with Decision 31/1999/Q§-UBCK3 dated
12 October 1999 by the Chairman of the State Securities Commission)
- Circular 01/1999/TT-UBCK1 dated 30 Dec. 1999 of the State Securities
Commission implementing Decision 139/1999/Q§-TTg dated 10 June
1999 of the Prime Minister on foreign ownership level in Vietnamese
securities market.
- Decree 01/2000/ND-CP dated 13 Jan. 2000 of the Government to promulgate
Regulation on Government bond issuance.
- Circular 01/2000/TT-UBCK1 dated 17 April 2000 of the State Securities
Commission, providing for temporary guidelines to securities businesses’
collection of fees from customers.
- Decree 17/2000/ND-CP dated 26 May 2000 of the Government on organization
and operation of securities inspection.
- Decree 22/2000/ND-CP dated 10 July 2000 of the Government on treatments
of administrative violations in the fields of securities and securities
markets
- Circular 02/2001/TT-UBCK, providing guidelines to Decree 48/1998/ND-CP
of the Government dated 7 Nov. 1998, on public offerings of stocks and
bonds.
PART II
GUIDELINES FOR SECURITIES MARKET DEVELOPMENT
FOR THE PERIOD 2001 -2010
1. Development and perfection of legal framework
for the securities market
- Promulgation of a new Decree replacing Decree 48/1998/ND-CP
The new Decree is drafted to replace Decree 48/1998/ND-CP to provide
broader and more comprehensive and appropriate coverage of market realities.
Implementing regulations are also amended to suit the prospective Decree
and other higher regulations, especially the Enterprise Law. Supplementary
regulations on trading of securities of small and medium sized companies
are also made.
- The making of “Securities Law “
It is expected that in 2003 after the 9th Congress’s approval,
a Law Construction committee will be established and headed by the State
Securities Commission and participated by relevant Ministries and agencies.
The Committee shall set up Drafting team to assist in preparing the
outlines and draft of the Securities Law. The Congress will consider
and pass the Law by 2005.
- Other relevant legal documents
The completion of amendments to regulations on regimes on finance, accounting,
auditing, tax, fees, levies, foreign exchange regulations applied to
participants in securities market shall be done in coordination with
relevant ministries and agencies.
Proposals for amendments to other legal documents relating to regulations
on securities markets such as Civil Code, Arbitration regulation, Ordinance
on resolutions of conflicts in economic crimes…shall be made to
authorized levels.
2. Supply boost for the market in terms of
quantity, quality and variety
- Large state owned enterprises, affiliates of general corporations
should be equitized and then listed in the securities market. The equitization
process should be tied to listing in the securities market. The State
Securities Commission are coordinating with the Enterprises Reform Committee
in constructing a procedures and choice of enterprises.
- Promulgation of a Decree to allow transformation of a number of Foreign
Direct Invested enterprises to joint-stock companies and enlisting thereof
(expected 15 to 20 enterprises)
- Listing of a number of joint-stock commercial banks.
- Continue to add further preferential treatments especially those
on tax on listed companies, securities companies, investment funds,
and foreign investors.
- Measures to be taken to encourage the establishment of venture capital
companies
- Encourage adding other types of products such as preferred stocks,
stock rights, Project bonds, corporate convertible bonds, investment
fund shares to listed market.
- Assist listed companies in applications of modern corporate governance
practices, accounting and auditing regimes in line with international
standards; Strengthen the regulation, supervision of listed companies
in compliance with information disclosure regime and other legal stipulations.
- Consider establishments of credit rating agencies with participation
of banks, insurance companies, securities companies (state owned or
foreign).
3. Strengthening of foreign and domestic demands
for securities
By measure to attract individual investors to the market; develop an
institutional investor base including investment funds, pension funds,
insurance companies, commercial banks. other financial institutions ;
encourage foreign investors’ participation in the market.
Consider policies to boost demand: (i) develop Employee- share-purchase
programs, (ii) relax restrictions and have tax incentives for credit institutions’
participation in the market; (iii) Speed up establishments of investment
funds and investment advisory companies; (iv) improve individual and retail
investors’ access to the market; (v) relax restrictions on foreign
securities investments….
4. Invest, upgrade technical
infrastructure and facilities, technologies related to securities. Promptly
organize a tender for provisions of IT system for securities market, separating
the depository center from the securities trading center as an independent
system, separating the TTGDCK from the State Securities Commission.
5. Prepare for starting the operation
of the Hanoi Securities Trading center (TTGDCK HN) for small and medium
– sized enterprises. In the future the TTGDCK HN shall become a
OTC market.
6.Strengthening of market transparency
- Perfecting the regulations on information disclosure, and process
thereof at the listed companies.
- Perfecting the information disclosure system of the TTGDCK and the
State securities commission; upgrading websites and other news medias.
7. Reinforcing the information
propagandizing activities and free of charge investor education for the
public; perfecting the education, examination, and practitioner license
system for securities markets.
8. Securities companies development
- Enhancements of capital size and expansion
of licensed activities of securities companies
Strengthening the potential and scale of operation of the securities
companies. It is expected that by year 2005 the minimum charter capital
of securities companies shall be increased to VND 20 billions. Toward
the year 2010, the securities companies will be classified into 2 types:
one providing brokerage and securities investment advises with minimum
charter capital of VND 5 billions; the other providing different types
of services and businesses with the minimum charter capital of VND 50
billions.
- Expansion of service branch network,
transaction offices and order taking agents of securities companies.
- Modernization of technical facilities
Modernization of information system, networking between securities companies
and securities trading centers and investors.
Development of centralized back-office of securities companies in lights
of cutting cost, improved information sharing for smooth management,
and improvement of transaction processing and easy future upgrading.
- Improve the quality of corporate governance,
brokerage services, securities professionalism
Improve the quality of corporate governance by strengthening the regulation
on financial prudence in securities companies, especially in proprietary
trading and underwriting activities; Apply corporate governance practices
in line with international standards; improve the quantity and quality
of practitioners.
9. Development of fund management companies
and investment funds
- Encourage fund management companies to increase their capital and
expand their operation geographically;
- Encourage the development of investment funds, especially those offering
shares publicly;
- Encourage establishment of joint ventures with foreign partners in
fund management business;
- Encourage foreign investors to invest in investment funds in Vietnam;
- Encourage foreign investment funds to participate in Vietnamese stock
market;
- Provide tax incentives to make sure that investments through funds
are not worse off than direct investment in the market.
10. Measures to be taken in 2003
In 2003, to gradually develop a stable, safe and sustainable market,
a number of immediate measure are to be taken:
- Increase of frequency of matching orders to 2 times per session, and
applying new type of orders
- Lower the size of a transaction unit from 100 shares to 10 share,
and lower the good-faith deposit ratio for placing orders
- Allow foreign investors to open accounts with securities companies
to facilitate their trading activities.
- Increase the share holding ratio for foreign individual and institutional
investors in listed companies to 30% (currently 20%)
- License 2 fund management companies.
|
 |

